High blood pressure symptoms, such as dizziness, chest pain, headaches, or pain in the back of the head, usually appear only when blood pressure rises very quickly. This can happen during periods of stress or after taking certain medications or drugs.
When blood pressure increases gradually over the years, known as hypertension, it rarely causes noticeable symptoms because the body adapts. For this reason, high blood pressure is often called a “silent disease.”
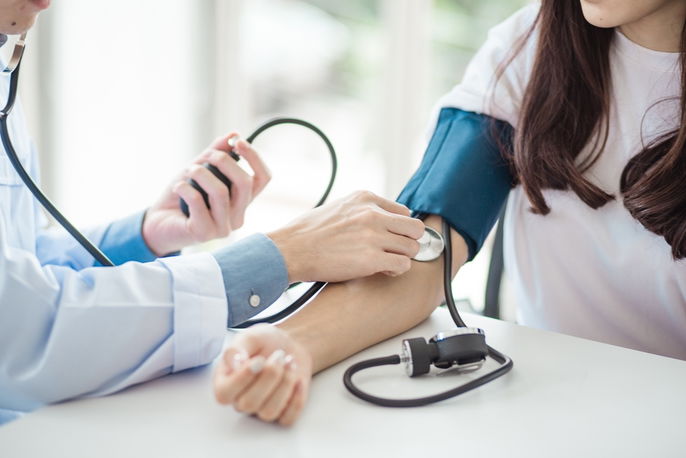
If high blood pressure is suspected, it is recommended to check blood pressure at home with a monitor or at a pharmacy. In U.S. guidelines, blood pressure between 120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic is classified as elevated blood pressure. Values of 130/80 mm Hg or higher fall into Stage 1 hypertension.
12 high blood pressure symptoms
The main symptoms that may indicate high blood pressure include:
1. Nausea
High blood pressure can rupture small blood vessels in the brain, increasing pressure inside the head. This can affect nervous system function and lead to nausea.
2. Headache
Increased blood pressure can reduce blood flow to the head and compress pain-sensitive nerves, which may cause severe headaches.
3. Chest pain
Chest pain can be a sign of high blood pressure because the heart has to pump with more force and speed, straining the heart muscles.
However, chest pain can also signal a heart attack, especially when accompanied by paleness, shortness of breath, coughing, or pain that radiates to the shoulder, neck, jaw, or arm. In these cases, immediate medical care is essential.
4. Dizziness
Dizziness can be a symptom of high blood pressure due to changes in blood flow and oxygen levels in the brain. This can affect balance and, in some cases, cause fainting.
It is important to note that dizziness may also occur as a side effect of medications used to treat hypertension.
5. Pain in the back of the head
High blood pressure may cause pain in the back of the head that spreads to the forehead, due to increased pressure compressing pain-sensitive nerves.
6. Weakness
Because high blood pressure reduces oxygen supply to the brain and forces the heart to work harder, it can cause weakness and drowsiness.
It can also reduce oxygen flow in the lungs, making breathing more difficult and leading to fatigue.
7. Ringing in the ears
Ringing in the ears, such as pulsing or beating sounds, may result from changes in blood flow in the arteries caused by high blood pressure.
8. Small red spots in the eyes
High blood pressure may cause blood vessels in the eyes to rupture, leading to small red spots.
9. Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath can occur with high blood pressure because reduced blood flow makes it harder to transport oxygen to the lungs.
10. Blurred or double vision
High blood pressure can cause hypertensive retinopathy, a condition that damages the blood vessels and nerves in the retina. This can lead to blurred or double vision or dark spots in the eyes.
11. Palpitations
Because high blood pressure narrows the arteries, the heart has to pump harder, which can cause palpitations or irregular heartbeats.
12. Nosebleeds
Although less common, nosebleeds may occur with high blood pressure because the tiny blood vessels in the nose can rupture easily when pressure increases.
High blood pressure symptoms in women
High blood pressure symptoms are the same in men and women. However, certain conditions, such as pregnancy, can raise the risk of high blood pressure, also known as preeclampsia. This condition may cause severe abdominal pain and swelling in the legs and feet.
In these cases, it is important to see an obstetrician as soon as possible to begin treatment and prevent complications such as bleeding or eclampsia.
Menopause also increases the risk of high blood pressure in women and can contribute to the appearance of symptoms.
Which doctor to see
If high blood pressure is suspected, it is best to consult a cardiologist. This specialist can evaluate symptoms and signs, review medical history, and recommend the most appropriate treatment if needed.
What to do to lower high blood pressure
To help lower high blood pressure, it is important to take medications prescribed by a cardiologist and rest. If blood pressure remains very high (for example, 180/120 mmHg or more) or if symptoms of organ damage appear (such as chest pain, shortness of breath, changes in vision, or neurological symptoms), immediate medical attention is required.
Otherwise, follow-up with your healthcare provider is recommended if readings stay above your treatment target.






























