- Yasmin is a combination oral contraceptive that prevents pregnancy by stopping ovulation and thickening cervical mucus.
- This medication offers additional benefits such as reducing hormone-related water retention and improving skin conditions like acne and oily hair.
- For maximum effectiveness, the pill must be taken at the same time every day for 21 days followed by a 7-day break.
Yasmin is a daily oral contraceptive pill designed to prevent pregnancy. It contains a combination of two female hormones, drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol, which work together to inhibit ovulation.
These hormones also create changes in the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to enter the uterus. By preventing both ovulation and fertilization, Yasmin provides a highly effective method of birth control.
The active ingredients in Yasmin also offer antimineralocorticoid and antiandrogenic benefits for many women. These properties help reduce hormone-related fluid retention and improve skin conditions like acne or oily hair.
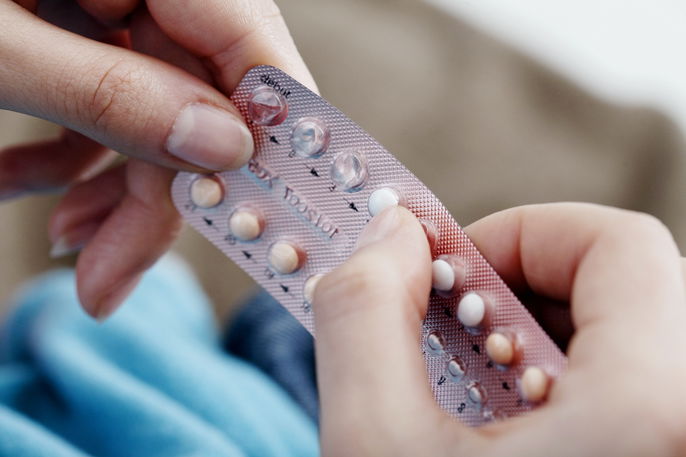
What it is used for
Yasmin is primarily prescribed as a contraceptive to prevent pregnancy. It achieves this by stopping the release of an egg from the ovaries and thickening the cervical mucus to block sperm.
Because of its specific hormonal balance, Yasmin can also help reduce bloating and water weight gain often associated with other pills. This makes it a common choice for women concerned about weight changes, while also helping to clear skin and manage excess oil.
In addition to preventing pregnancy, Yasmin helps regulate menstrual cycles and decrease heavy bleeding. This can lower the risk of iron deficiency anemia and significantly reduce the pain associated with menstrual cramps.
How to take Yasmin
You should take one Yasmin tablet every day at the same time for 21 consecutive days. Follow the arrows on the blister pack to ensure you are taking the pills in the correct order.
After finishing a 21 day pack, you must take a 7 day break before starting your next pack. During this one week interval, you will typically experience a withdrawal bleed similar to a period.
If this is your first time using hormonal birth control, take your first pill on the very first day of your menstrual period. While Yasmin is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, it does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), so you should still use condoms.
What to do if you miss a dose
If you realize you missed a pill but it has been less than 12 hours since your scheduled time, your protection is not affected. Take the missed pill immediately and take your next pill at the usual time.
If more than 12 hours have passed, follow the guidelines based on which week of the pack you are in:
Week 1
-
Take the missed pill immediately and continue the pack as usual.
-
Use backup birth control? Yes, for the next 7 days.
-
Risk of pregnancy? Yes, if you had unprotected sex in the 7 days before the miss.
Week 2
-
Take the missed pill immediately and continue the pack as usual.
-
Use backup birth control? Only if you also missed pills during Week 1.
-
Risk of pregnancy? No, if Week 1 was taken correctly.
Week 3
-
Either start a new pack immediately (skipping the break) OR stop the current pack, wait 7 days, and start a new one.
-
Use backup birth control? Only if you also missed pills during Week 2.
-
Risk of pregnancy? No, if Week 2 was taken correctly.
If you miss more than one pill in a single pack, consult your gynecologist. If you vomit or have severe diarrhea within 4 hours of taking a pill, use a backup method like condoms for the next 7 days.
Possible side effects
Common side effects associated with Yasmin include mood swings, depression, and a decreased interest in sex. Some users may also experience migraines, nausea, or breast tenderness.
Weight gain and breakthrough bleeding (spotting between periods) are also possible. If these side effects become severe or persistent, contact your healthcare provider to discuss your options.
Who should not use Yasmin
Yasmin is not suitable for everyone and should be avoided if you are pregnant or currently breastfeeding. It is also contraindicated for individuals with severe kidney disease or uncontrolled high blood pressure.
You should not take Yasmin if you have a history of blood clots, heart attack, or stroke. It is also unsafe for those with severe liver disease, a history of migraines with aura, or suspected hormone dependent cancers like breast or uterine cancer.
Women over the age of 35 who smoke should avoid Yasmin due to a significantly increased risk of serious cardiovascular events. Always disclose your full medical history and any allergies to your doctor before starting this medication.






























