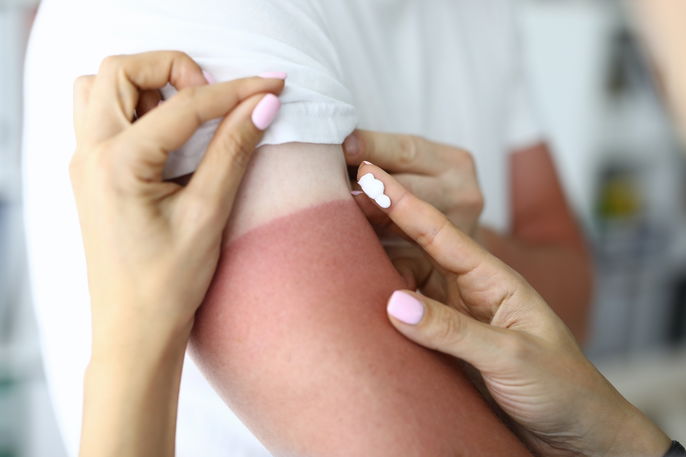
Ointments for burns, such as dexpanthenol or hydrocortisone, can be used to treat first-degree burns that cause redness, swelling, pain, or discomfort on the skin. These products help relieve pain and inflammation, promote healing, and prevent infection.
First-degree burns usually happen after contact with extreme heat, such as touching a hot pan, or from sun exposure without sunscreen. They can also occur due to contact with extreme cold or certain chemicals.
These ointments are available at most pharmacies and drugstores, and many can be purchased without a prescription. However, antibiotic ointments generally require a doctor’s prescription. They are best suited for mild first-degree burns that do not involve blisters or peeling.
Main ointments for burns
The main ointments that may be recommended by a healthcare provider for treating burns include:
1. Dexpanthenol
Dexpanthenol ointment is recommended for first-degree burns without blisters. It helps regenerate skin cells and provides moisturizing, protective, and nourishing effects thanks to its vitamin B5 content, which supports skin healing.
This ointment can be found under the brand name Bepanthen in the United States and should be applied to the burn 1 to 3 times a day.
2. Neomycin sulfate + bacitracin zinc
The combination of neomycin sulfate and bacitracin zinc acts as an antibiotic that prevents infections and supports skin healing after mild burns.
This cream is available with a prescription and can be found under brand names such as Neosporin or as a generic neomycin and bacitracin zinc ointment. It should be applied 2 to 5 times daily using a sterile gauze pad, following a healthcare provider’s instructions.
3. Hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone cream is a corticosteroid with anti-inflammatory properties that helps reduce redness, swelling, and discomfort, promoting skin recovery. It is typically indicated for first-degree burns caused by sun exposure.
This cream can be applied 1 to 2 times daily as directed by a healthcare provider. It should not be used on large areas of skin or for prolonged periods, as it may cause side effects such as blurred vision, eye pain, increased thirst or urination, dry mouth, weight gain, facial swelling, muscle weakness, mood changes, or irritability.
4. Silver sulfadiazine
Silver sulfadiazine cream is used to treat and prevent infections in burn wounds. It has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that promote healing.
This medication is available with a prescription and is commonly sold under brand names such as Silvadene or SSD cream. Silver sulfadiazine should be applied 1 to 2 times a day and is generally recommended for more serious second- or third-degree burns after evaluation by a healthcare professional.
5. Bacitracin or neomycin ointment
An ointment containing bacitracin or neomycin helps prevent bacterial infections and promotes the formation of new skin cells, supporting the healing process. These ointments are typically recommended for mild burns.
They require a prescription when combined with certain ingredients and should be applied 1 to 2 times daily according to medical advice.
6. Silver sulfadiazine or bacitracin
For burns caused by sun exposure or contact with hot surfaces, an antibacterial ointment such as silver sulfadiazine or bacitracin can help prevent infections and promote healing.
These creams are available with a prescription and should be applied as directed by a healthcare provider, usually in a thin layer over the affected area.
7. Moisturizing cream with collagen and vitamins A & E
A cream containing collagen and vitamins A and E has moisturizing, healing, and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps reduce redness, pain, and discomfort caused by sunburns or burns from treatments such as radiotherapy, chemical peels, or laser hair removal.
These creams can be applied in a thin layer up to 5 times a day, or as advised by a healthcare professional.
8. Madecassoside
Madecassoside, a compound derived from Centella asiatica, has moisturizing and reparative effects that help restore the skin’s protective barrier.
Ointments containing madecassoside often also include panthenol, zinc, copper, and manganese, which promote regeneration and help prevent bacterial infections. A similar product available in the US is Cicaplast Baume B5+ by La Roche-Posay, which can be used for first-degree burns.
When not to use burn ointments
Most over-the-counter burn ointments are safe for use without medical supervision. However, pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and people with sensitive skin or known allergies should always consult a healthcare provider before using them.
How to treat a first-degree burn
First-degree burns are generally mild and easy to treat. To manage them safely:
-
Wash the affected area thoroughly and, if possible, run cool (not cold) water over it for 5 to 15 minutes.
-
Apply cool compresses to the area while pain or swelling persists. Compresses can be soaked in cold water or chilled chamomile tea to help soothe the skin. Never apply ice directly, as it can worsen the burn.
-
Apply a healing ointment or antibiotic cream 1 to 3 times a day for 3 to 5 days, following a healthcare provider’s instructions.
If blisters develop or the skin begins to peel, seek medical attention to prevent infection and ensure proper healing.
It is also important to avoid applying oil, butter, coffee grounds, or toothpaste, as these can worsen the burn and increase the risk of infection, delaying recovery.






























