VO2 max is the amount of oxygen your body can use during aerobic exercise, and it’s one of the main indicators of both overall fitness and cardiopulmonary health. This measurement shows how efficiently your body can deliver oxygen to your muscles while you’re active.
Also called maximum oxygen volume, VO2 max varies based on factors such as age, sex, and body weight. In general, higher values indicate a better ability to perform sustained aerobic exercise.
To measure your VO2 max, you should consult a cardiologist, pulmonologist, or primary care provider. These professionals can recommend the most appropriate tests for evaluation and advise on ways to safely improve your results.
What is a normal VO2 max
In most cases, a VO2 max above 80% of what is predicted for your age, sex, and body weight is considered normal. However, there is no strict consensus on ideal VO2 max values.
Generally, higher VO2 max values are associated with better aerobic fitness and cardiopulmonary health.
VO2 max chart for men
Approximate VO2 max values for men by age:
When VO2 max is above the corresponding value for a person’s age group, it’s generally considered acceptable, good, or excellent depending on how high it is. Values below are usually considered low.
For example, a sedentary man typically has a VO2 max between 30 and 35 mL/kg/min, while marathon runners often reach about 70 mL/kg/min.
VO2 max chart for women
Approximate VO2 max values for women by age:
As with men, values above the listed range for each age group are considered acceptable, good, or excellent as they rise. Lower results tend to be considered poor.
Women generally have slightly lower VO2 max values than men, ranging from 20 to 25 mL/kg/min among sedentary women and up to 60 mL/kg/min among athletes. This difference is primarily due to naturally higher body fat percentages and lower hemoglobin levels.
How to measure VO2 max
VO2 max can be measured directly or indirectly using the following tests:
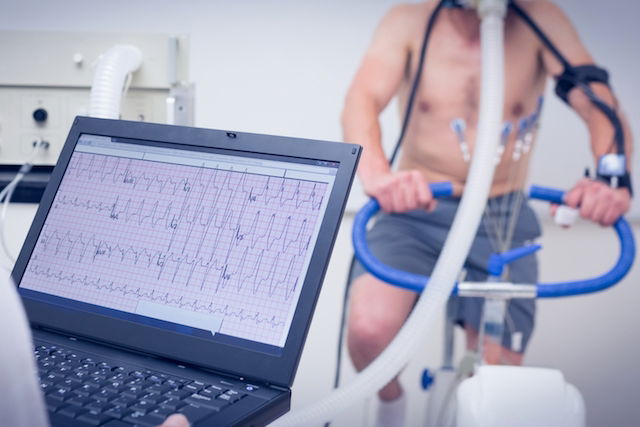
1. Ergospirometry
Ergospirometry, sometimes called a pulmonary capacity test, is performed on a treadmill or stationary bike while you wear a mask and monitoring electrodes. It directly measures gas exchange during breathing and also tracks heart rate and exercise effort.
This test is typically ordered by cardiologists or sports medicine physicians and is often used to evaluate athletes or assess lung or heart conditions.
2. Cooper test
The Cooper test estimates VO2 max indirectly by measuring the distance a person can walk or run in 12 minutes at maximum effort. After noting the total distance, a calculation is used to estimate VO2 max.
How to increase VO2 max
Strategies commonly recommended to improve VO2 max include:
-
HIIT workouts that alternate short bursts of high-intensity exercise with periods of lower intensity
-
Exercises like running, walking, or cycling, especially with the goal of improving your time or pace
-
Weight loss when appropriate, since VO2 max calculations are partly based on body weight
Most people can increase their VO2 max by up to about 30%. This improvement usually comes from building cardiovascular endurance so the body can take in and use oxygen more efficiently.
Training at about 85% of your maximum heart rate can significantly improve VO2 max, but this level of intensity is not recommended for beginners.
People who are just starting to exercise should begin with lighter routines designed and supervised by a certified fitness professional.






























