A bump on the eyelid can appear with conditions like a chalazion, stye, xanthelasma, dacryocystitis, shingles, or in rare cases tumors. These bumps may cause redness, swelling, pain, or small nodules that slowly increase in size.
Depending on the cause, a bump on the eyelid may improve with warm compresses, gentle massage, or simple home care. Some situations may require antibiotics, antiviral medication, or procedures such as drainage or surgical removal.
A bump on the eyelid that does not improve, becomes painful, or continues to grow may indicate an underlying condition that needs medical evaluation. An ophthalmologist can identify the cause and recommend the most appropriate treatment to prevent complications.
Why do I have a bump on my eyelid?
The main causes of bumps on the eyelid:
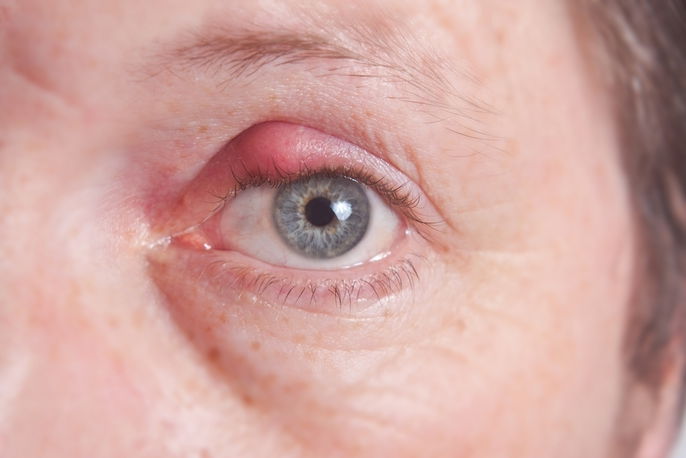
1. Chalazion
A chalazion is inflammation of the eyelid that occurs due to obstruction of the glands, causing the appearance of a nodule, pimple or bump. It is most commonly seen on the upper eyelid and tends to grow slowly and without causing pain.
What to do: Chalazions tend to improve after about one month with simple measures, such as applying warm compresses to the affected eyelid for 15 minutes, 2 to 4 times a day. You can also lightly massage the area.
You are advised to see an ophthalmologist when symptoms persist or if new ones appear, such as pain and difficulty seeing. In these cases, the use of eye drops with antibiotics or surgery may also be indicated.
2. Stye
A stye or hordeolum is normally caused by a bacterial infection of the root of the eyelashes on the eyelid, causing the appearance of a painful nodule, similar to a ball or pimple in the eye. Other symptoms include the accumulation of pus, redness and swelling of the affected eyelid.
What to do: the stye usually improves without specific treatment in around 2 weeks. You can apply warm compresses to the eyelid and massage the area lightly to stimulate the drainage of the secretion. Learn more about how to get rid of a stye.
However, if the stye takes a long time to improve or if it is very large, you should consult an ophthalmologist. Furthermore, if the swelling worsens or a fever develops, you should seek urgent medical attention.
3. Xanthelasma
A xanthelasma is a yellowish ball in the eye that appears due to the accumulation of cholesterol. Typically, the ball develops on the upper eyelid, in the part closest to the bridge of nose. It is more common in people over 40 and with high cholesterol.
What to do: Although xanthelasma bumps usually don't go away, they aren't considered a health problem. It is possible to consult a dermatologist, who may recommend treatment with cryotherapy, application of acids, or surgical removal.
Furthermore, it is important to control blood cholesterol levels, and treatment with medications, such as statins, and measures such as reducing the consumption of fatty foods and losing weight may be indicated.
4. Dacryocystitis
A small bump on the eyelid caused by dacryocystitis is associated with inflammation of the tear sac. The bump tends to form in the corner of the eyelid closest to the bridge of the nose, and can resemble a pimple on the eye. It causes pain, swelling and redness in the area.
What to do: if you suspect your may have dacryocystitis, you should consult an ophthalmologist. Treatment may involve simple measures such as applying warm compresses and massaging the affected area. In more serious cases, antibiotics may be prescribed.
5. Shingles
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is an infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It can cause small bumps to appear on the eye, especially on the upper eyelid and forehead.
It is also common for other symptoms to appear, such as skin redness, drooping eyelids and a burning or tingling sensation.
What to do: Bumps caused by herpes zoster tend to disappear with the treatment of the infection, which usually involves the use of antiviral medications, such as acyclovir or valacyclovir, as recommended by the ophthalmologist.
6. Tumors on the eyelid
Although they are rare, some tumors on the eyelid can cause a small bump or pimple to appear on the eye, which tends to increase in size over time. The bump can be confused with a chalazion or stye, but it generally does not improve with treatment or appears again.
What to do: If you suspect you may have an eyelid tumor, it is important to consult an ophthalmologist or dermatologist for an evaluation, and a biopsy may be indicated to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment of eyelid tumors is usually done through surgery.
Which doctor to consult
Bumps on the eyelid are assessed by an ophthalmologist, who can carry out an eye examination to identify the underlying cause of the bump and indicate the most appropriate treatment.
Typically, the ophthalmologist performs specific tests, such as refraction and fundus examination, to help with the diagnosis.






























