Fibromyalgia is a chronic neurological condition that causes pain in the whole body, as well as increased sensitivity to pain. Since the discomfort caused by fibromyalgia persists for several months, and even years, people who have this condition also have a higher tendency to feel fatigued and develop sleep disorders and/or psychological problems.
This condition is more common in women and the first symptoms usually appear in adulthood between the ages of 30 and 50.
There is no cure for fibromyalgia, but treatment, when guided by a rheumatologist, can help to improve quality of life.

Main symptoms
The main symptom of fibromyalgia is pain felt from head to toe, however, other symptoms may also be present, such as:
- Increased sensitivity in some areas of the body;
- Fatigue;
- Muscle rigidity;
- Recurrent headaches;
- Sleep problems;
- Memory and concentration problems.
In some cases, more rare symptoms can also arise, such as tingling in the hands and feet, pain in the jawbone or digestive problems, especially irritable bowel syndrome.
It is also common to have brain fog, in which the person has difficulty focusing. This affects the person's memory and concentration capacity. For that reason, people with fibromyalgia also present a higher risk of developing depression and other psychological conditions.
Fibromyalgia trigger points
Fibromyalgia is known for causing increased sensitivity in some "trigger points". These trigger points are:
- The upper part of the shoulders;
- Nape of the neck;
- Lateral parts of the hips;
- Knees;
- Elbows.
In the past, these points were normally used as a form of diagnosing fibromyalgia, as the doctor put pressure on the points to identify if the person felt more pain than normal. Nowadays, it is not as common to use these trigger points as a way to reach a diagnosis.
How to confirm the diagnosis
Usually, diagnosis is confirmed by a rheumatologist, but it can be a lengthy process as there is not one sole test or exam that leads to a confirmed diagnosis. For that reason, many people end up suffering from fibromyalgia for several months without knowing the actual cause. Diagnosis usually happens after the doctor assesses all presenting symptoms and rules out other possible conditions, such as hypothyroidism or polymyalgia rheumatica.
The doctor will usually order x-rays and blood tests to help with diagnosis.
What causes fibromyalgia
The specific cause of fibromyalgia is not yet known, however, it is possible that the condition is caused by a neural alteration, which affects the way pain is understood by the nervous system.
There are also some factors that seem to increase the risk of developing fibromyalgia, such as:
- Family background of fibromyalgia;
- Lupus or rheumatoid arthritis;
- Stressful situations;
- Repeated blows to a certain part of the body;
- History of viral infection.
In addition, women over 30 are at an increased risk for fibromyalgia, even though the condition can appear in people of all genders and at any age.
Treatment options
There is no cure for fibromyalgia, however, with the correct treatment supervised by a rheumatologist, it is possible to relieve the symptoms and manage the disease. Common treatments include:
1. Medication for fibromyalgia
There are three types of medication that can be prescribed for treating fibromyalgia:
- Antidepressants, such as amitriptyline or fluoxetine: increase the concentration of some neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which help control the pain;
- Muscle relaxants, such as cyclobenzaprine: help to relieve muscle rigidity, encouraging body relaxation and helping with pain relief;
- Analgesics, such as tramadol: act directly on the pain.
When the treatment with these medications does not present the desired effect, the doctor may assess the use of other substances, such as antiparkinsonian drugs, which have an effect on the central nervous system and can also help decrease the pain caused by fibromyalgia.
2. Cognitive behavioral therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a type of psychotherapy that aims to help a patient with fibromyalgia identify emotions and day-to-day situations that seem to worsen the fibromyalgia pain. This type of therapy is important to decrease stress levels, which, when elevated, can worsen fibromyalgia symptoms.
3. Regular physical activity
Physical activity is also important in the treatment of fibromyalgia. It is imperative, however, that the patient follows the recommendations of the doctor and of the physical education specialist by doing exercises that help relieve the pain and strengthen and stretch the muscles, such as walking, swimming and hydro gymnastics, three to five times a week, for 30 to 60 minutes.
4. Physical therapy
To improve movements, the doctor may also prescribe physical therapy sessions for fibromyalgia, at least twice a week. These sessions can include therapeutic massages, stretches and relaxation exercises, which help reduce the symptoms by encouraging local analgesics and improve blood circulation.
5. Anti-inflammatory diet
An anti-inflammatory diet can be a good option for those who have fibromyalgia, as it helps decrease any nerve or muscle inflammation. Thus, it is recommended that you have a diet rich in magnesium, potassium and omega 3 to help relieve the symptoms:
- Magnesium, present in foods such as avocado, artichoke and seeds: helps to relax muscles and improve circulation;
- Potassium, in foods such as banana, apple, beetroot and peas: helps to avoid muscle weakness and cramps;
- Omega 3, present in sardine, salmon and chia seeds: has an anti-inflammatory effect and relieves pain symptoms.
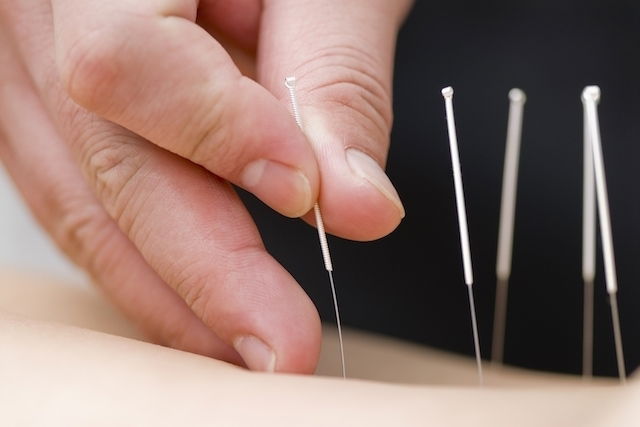
6. Acupuncture
Acupuncture consists of applying needles in specific points of the body to relieve pain. However, there is still no consensus about the effectiveness and therapeutic action on fibromyalgia, and so it may have an effect on some patients and not on others.
Natural treatment for fibromyalgia
Natural treatment with medicinal plants is another therapy that may be indicated to complement the treatment prescribed by the doctor. Some of the common plants are perforate St John's-wort which has a similar effect as some anti-depressants, Ginkgo Biloba, which increases oxygenation and blood circulation and turmeric, which has a strong anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
Possible complications of fibromyalgia
The main complication of fibromyalgia is brain fog, which happens when the pain is constant and affects the brain's reasoning ability, causing the person with fibromyalgia to find it hard to think, concentrate and even memorize information. As such, there is also a greater risk of developing psychological conditions such as depression.
In addition, people with fibromyalgia present a high rate of hospitalization for other health problems.
