Trypophobia is a psychological disorder characterized by an irrational fear of images or objects with holes or irregular patterns, such as honeycombs, holes on the skin, wood, plants, or sponges.
People who suffer from this fear feel terrible when confronted with these patterns and may experience symptoms like itchiness, shivers, tingling, and repulsion. In more serious cases, trypophobia can lead to vomiting, increased heart rate, and even panic attacks.
Treatment can include gradual exposure therapy, anxiety medication, antidepressants, or psychotherapy.
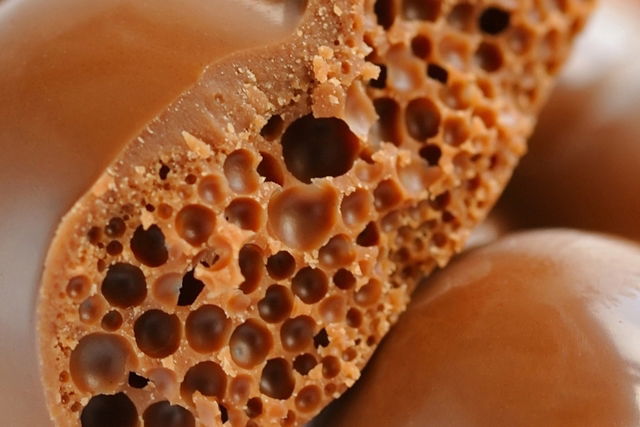

Main symptoms
People with trypophobia may present with the following symptoms when exposed to patterns such as lotus seeds, honeycombs, bubbles, strawberries, or crustaceans:
- Nausea;
- Shivering;
- Sweating;
- Crying;
- Chills;
- Discomfort;
- Increased heart rate;
- Itchiness and tingling.
In more serious cases, the person may also have panic attacks due to an extreme level of anxiety.
What causes it
Generally, people who suffer with trypophobia cannot consciously distinguish safe situations from dangerous one. The uncontrollable reactions they experience are often an unconscious reflex.
Trypophobia triggers
According to research, people with trypophobia unconsciously associate holes or objects that have irregular patterns with dangerous situations. Objects that most commonly trigger symptoms are those found in nature. This happens due to the similarity of the holes with the skin of venomous animals, such as snakes or with maggots that can cause skin diseases.
Treatment options
Treatment for trypophobia should be guided by a psychologist and/or psychiatrist according to the degree of the phobia and symptoms presented by the person.
1. Exposure therapy
This type of therapy helps the person to control their fear and change their response to the trigger. It must be done very carefully so that it does not cause additional trauma.
This therapy should be carried out with the help of a psychologist through gradual exposure to the stimulus that causes the phobia. Through dialogue, the therapist uses relaxation techniques to help the person face their fear until the discomfort subsides.
2. Use of medications
Medications may be prescribed by a psychiatrist as a complement to exposure therapy. Typically anxiety medications, like sedatives and beta-blockers.
Also recommended: 10 Natural Remedies for Anxiety (& How to Prepare) tuasaude.com/en/natural-remedies-for-anxiety3. Engage in activities that promote well-being
Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and reduce anxiety can also be recommended by a psychologist or psychiatrist. Some beneficial activities include yoga and exercise.
