Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes characteristic symptoms such as red, dry patches, that can itch ou cause a slight burning sensation or pain.
Even though this type of condition is relatively common, the exact cause is yet unknown. However, the patches seem to appear or become more intense in situations that directly affect immunity, such as periods of great stress or auto-immune diseases.
If you suspect you have psoriasis, you should see a dermatologist for assessment of your skin. The doctor may rule out other skin conditions before advising treatment, which may include a combination of medication, phototherapy and diet.

Common symptoms
The main symptoms of psoriasis are:
- Red plaques or spots on the skin
- Skin peeling in the affected area, similar to dandruff
- Itching or burning
- Dry skin o
- Skin cracks that can bleed.
Psoriasis symptoms can appear on the arms, elbows, hands, legs, knees, genitals, scalp, belly, coccyx or lower back and vary according to the type of psoriasis.
Also recommended: Red Spots On Skin: Top 19 Causes (with Pictures & Treatment) tuasaude.com/en/red-spots-on-skinHow long does psoriasis last on the skin?
The duration os psoriasis symptoms can vary, as symptoms are cyclical and appear in flare-ups. They can last for a few weeks to months, and disappear after some time without requiring treatment, however they may reappear, again especially during periods of greater stress.
Types of psoriasis
Most cases of psoriasis are characterized by the presence of red, dry patches on the skin. However, depending on the location affected, psoriasis can be divided into various sub-types that can cause other symptoms to appear:
1. Common psoriasis
Common psoriasis, also known as plaque psoriasis, is the most common form of the condition and is characterized by red patches with white or silvery scales, or plaques that can be a few millimeters long.
This type of psoriasis usually affects the legs, arms, scalp, and lower back region, but it can also affect the nails. Other symptoms such as itchiness or burning can also appear, varying from one person to another.
2. Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis, also known as eruptive psoriasis, is more common in children, teenagers, and young adults, and it is characterized by patches with a drop-like appearance on the skin.
The patches are smaller than 1 centimeter and they tend to appear on the upper body, armpits, and in the groin area, generally after a streptococcus infection of the respiratory tract.
3. Pustular psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis happens when little pus-filled blisters appear on the skin, together with the psoriasis patches. These blisters can appear in just one specific area of the skin, or they can spread all over the body. When pustular psoriasis is generalized, the person may experience a fever of 102.2º F (39º C) to 104º F (40º C) for several days.
4. Inverse psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis is another type of psoriasis which is easily identified because the patches occur in humid areas of the body, such as armpits, groin area, inflammatory region, belly button, or scalp. As they occur in humid locations, these patches do not usually get dry or scaly skin.
5. Nail psoriasis
Nail psoriasis happens when the disease affects the nail area, causing ridges or patches on the nails, and weak nails.
Many times, nail psoriasis appears before psoriasis flares up on the skin, and it may be the only symptom for several years.
6. Scalp psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis or head psoriasis, causes the classic symptoms of psoriasis and can also lead to hair loss in the affected area of the scalp.
Symptoms can also spread from the scalp to the ears, neck, neck or face, mainly affecting the forehead, which can then be referred to as face psoriasis.
7. Genital psoriasis
Genital psoriasis can affect areas such as the pubis, thighs, buttocks, anus, penis or vulva.
This type of psoriasis causes intense itching or irritation in the genital area, which can be more intense when the person sweats and/or frequently wears warm, tight clothing.
8. Palmoplantar psoriasis
Palmoplantar psoriasis affects the palms of the hands and/or the soles of the feet and causes symptoms such as red, dry patches, itching, burning, pain and cracks in the skin.
When it affects the skin of the feet, it is popularly known as foot psoriasis. When it affects the hands, it is called hand psoriasis.
Palmoplantar psoriasis can make activities of daily living, such as walking, putting on shoes or picking up objects, more difficult.
9. Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is the development of chronic inflammatory arthritis in people who have psoriasis, affecting the joints and causing pain mainly in the toes or hands.
However, this type of psoriasis can also affect the hip joints, spine or knees, and may appear in association with skin psoriasis or nail psoriasis.
10. Erythrodermic psoriasis
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a type of psoriasis in which symptoms affect about 90% of the body surface and usually cause severe itching, pain or swelling.
This type of psoriasis is an exacerbation of plaque psoriasis, which can arise due to the abrupt cessation of corticosteroid use.
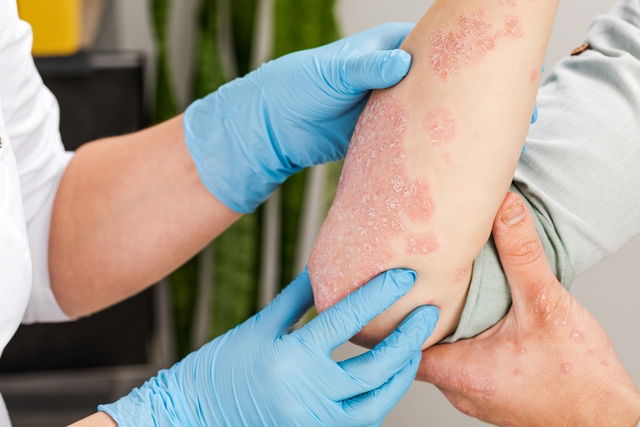
How is psoriasis diagnosed
Psoriasis is diagnosed by a dermatologist through a symptom assessment. The doctor will consider when they started, how long they last, the symptoms severity, and patient's health history, followed by a physical examination of the skin, nails and scalp.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may have to order additional tests to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as eczema, ringworm, lichen planus or lupus erythematosus.
Also recommended: Eczema: Symptoms, Causes, 9 Types & Treatment tuasaude.com/en/eczemaCommon causes
The specific causes of psoriasis are not known, however, it is considered to be an autoimmune disease and regulated by T-lymphocytes. It can also be influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
Some factors that seem to increase the chances of developing psoriasis include:
- Blows to the skin
- Sun burns or insect bites
- Cuts, scratches, chemical or radioactive injuries
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Habits like smoking or drinking a lot of alcohol
- Emotional stress
- Use of medication, especially antimalarial, lithium or beta blockers.
Psoriasis also presents a strong genetic link, as over 50% of people affected have cases of psoriasis in the family.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is not contagious and is not caused by viruses, fungi or bacteria, although some infections can trigger psoriasis attacks in people who have the disease.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition, which means that the immune system attacks its own skin cells as if they were foreign invaders.
Treatment options
There is no known treatment available to completely cure psoriasis. There are, however, various types of treatment that can relieve the symptoms and improving life quality.
The main types of treatment are:
1. Psoriasis medications
Medications that the doctor can prescribe for psoriasis include mainly corticosteroids, immunosuppressants or biological agents, such as hydrocortisone, tacrolimus, methotrexate, cyclosporine or adalimumab.
These remedies can be used in the form of tablets, injections or ointments for psoriasis, and help to manage symptoms and reduce the immune responses to reduce the inflammatory process in the skin. Check out the complete list of psoriasis medications that are typically prescribed for this condition.
In addition, there are also some home remedies for psoriasis, which can be used with medical supervision to control the symptoms, without adding side-effects to the treatment. A good example of this is watercress, which helps the body eliminate substances which could cause psoriasis crises or aggravate symptoms. Read more about home remedies for psoriasis that you can use to complement your medical treatment.
2. Phototherapy
Phototherapyconsists of applying UVB rays on the skin and it is normally used in conjunction with medication and lotions to increase the anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effect;
3. Diet
A psoriasis diet is another way of complementing medical treatment of psoriasis, which is made-up of anti-inflammatory foods that help to reduce skin swelling, skin lesions and skin flare-ups.
Also recommended: Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Food List & Sample 3-Day Meal Plan tuasaude.com/en/anti-inflammatory-dietIs psoriasis curable?
There is no cure for psoriasis, as there are still no medications available that completely eliminate psoriasis.
However, the symptoms of psoriasis can be managed with treatment as prescribed by a dermatologist, which can help to prevent new flare-ups.
