What is it:
Genital psoriasis, or inverse psoriasis, is an autoimmune disease that affects the skin in the genital area, causing smooth, red patches that look dry.
This skin condition can affect both men and women and can develop in any part of the genital area, including the pubic area, thighs, buttocks, penis, or vulva.
Even though it has no cure, it is possible to manage genital psoriasis with appropriate treatment prescribed by a dermatologist or immunologist.
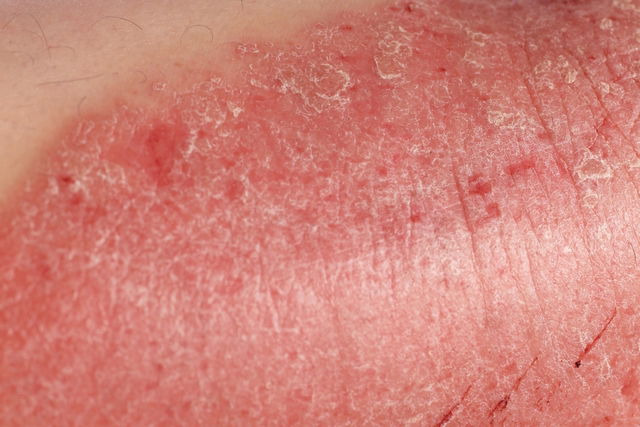
Common symptoms
The most common symptoms of genital psoriasis include:
- Small smooth, red, and shiny patches in the genital area;
- Intense itchiness in the area;
- Dry and irritated skin.
These symptoms generally appear in people who are overweight. Symptoms tend to worsen with sweat and frequent use of warm, tight-fitting clothes.
How to confirm the diagnosis
It is usually easy to diagnose genital psoriasis. A diagnosis is usually confirmed by a dermatologist following an assessment of the skin and the presenting symptoms.
The doctor may also order tests to rule out other causes for dry skin flare-ups, like bacterial or fungal swabs.
What are the most affected areas?
The most affected areas of genital psoriasis include:
- Pubis: affects the area above the genitalia where there is hair, and symptoms are similar to scalp psoriasis;
- Thighs: patches usually appear in the groin area, near the genitalia;
- Vulva: these patches are usually red and smooth and are only on the external part of the vagina;
- Penis: psoriasis usually occurs on the glans (head), but it can also affect the body of the penis;
- Buttocks and anus: the patches appear near the anus, causing intense itchiness;
- Armpits: symptoms get worse with tight-fitting clothes and sweat;
- Breasts: the patches usually appear in the bottom part of the breasts.
In men, genital psoriasis does not cause sexual dysfunction, however, the condition may cause anxiety which can interfere with intercourse. Also, some of the medications used for treatment can have side effects which can affect erection.

Treatment options
Genital psoriasis is usually treated with a topical corticosteroid cream which should only be used as prescribed over the affected area to decrease skin inflammation and relieve discomfort.
In more serious cases, in which the patches do not improve with creams or when other body areas also get affected, the dermatologist may prescribe oral medication.
Another alternative is UV light therapy, which consists of the application of UVA and UVB rays directly on the affected areas. This type of treatment is done in specialized dermatology clinics, and the duration and number of sessions depend on the skin type and the seriousness of the lesions.
Tips for a quick recovery
The following tips will help with skin irritation and quick recovery after a flare-up:
- Wearing light, cotton clothes that are not tight-fitting;
- Avoid sweat in the area, and re-apply psoriasis cream immediately after showering or doing physical activity;
- Keep the affected area clean at all times;
- Avoid using perfume, soap, and creams not prescribed by a doctor;
- Avoid using perfumed panty liners or pads, as these can irritate the skin;
- Wash and remove prescription cream from your genital area before having intercourse;
- Wear a condom and lubricate the area well during intercourse;
- Wash your genitals after intercourse and reapply your prescription cream.
It's also important to remember that coal tar-based creams should only be applied in the genital area under doctor orientation, as using these in excess can make your skin more irritated and cause worsening flare-ups.
