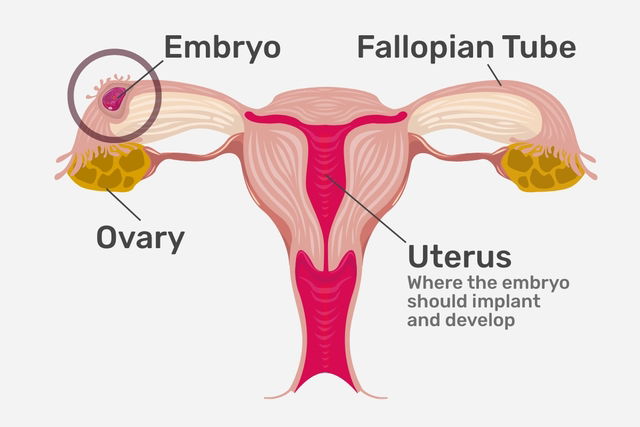
An ectopic pregnancy is when the embryo implants and develops outside the of uterus, such as in the fallopian tubes, ovaries, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
Signs of ectopic pregnancy include intense abdominal pain and blood loss through the vagina, especially in the first trimester. These symptoms require immediate assessment by your obstetrician, otherwise you should proceed to the emergency room.
The exact location of the embryo is important to determine the best treatment approach. Development of an embryo in the abdominal cavity, for example, more rare, but can result in longer viability and can serious health complications for the mother.
Main symptoms
A ruptured ectopic pregnancy happens when the embryo develops in the fallopian tubes to size big enough to burst them. This type of ectopic pregnancy presents very differently than one that occurs outside the fallopian tubes. A ruptured ectopic pregnancy will is typically associated with:
- Intense abdominal pain;
- Irregular vaginal blood loss, especially between week 5 and week 14;
- Feeling of weight pr pressure on the vagina;
- Intense pain when touching the lower abdomen;
- Swollen abdomen;
- Beta HCG test usually negative.
Ectopic pregnancies without rupture are associated with:
- Light abdominal pain or discomfort;
- Vaginal bleeding;
- Strong pain when touching the womb area;
- Pain during sexual intercourse or during a pelvic exam;
- Beta HCG test usually positive.
If you suspect you might have an ectopic pregnancy you should proceed to the hospital immediately. An ultrasound will likely be ordered to confirm if the embryo is developing outside the uterus.
Due to the development of the baby, and it's growing size, ectopic pregnancies are almost always discovered in the first 14 weeks of pregnancy.
How is treatment done
Treatment for an ectopic pregnancy is usually guided by an obstetrician and will usually depend on the exact location of the embryo. The pregnancy is usually not viable if the embryo develops outside of the womb, and therefore treatment is aimed at terminating the pregnancy while preserving the health of the woman.
Termination of pregnancy can be done with medication or with a surgical procedure to both remove the embryo and reconstruct the fallopian tube if needed. When the ectopic pregnancy is discovered before eight weeks of pregnancy, the embryo is still very small and the doctor can often prescribe a medication, called methotrexate. to induce abortion. When pregnancy is more advanced, a surgical procedure to remove the embryo is usually necessary.
