Scabies is an infectious disease caused by the Sarcoptes Scabiei mite, which attacks the skin and causes symptoms like intense itching and redness.
This disease is easily transmitted between members of the same household by sharing clothes, bed linens or towels. Avoiding direct contact with infected skin is advised, at least until treatment is completed. Although it is more frequent in family, scabies mites do not attach to dogs, as dog mites are different species.
Scabies is curable with the right treatment, prescribed by a dermatologist. Treatment usually involves the use of medications like permethrin and benzoyl, which help to eliminate the mite and relieve associated symptoms.
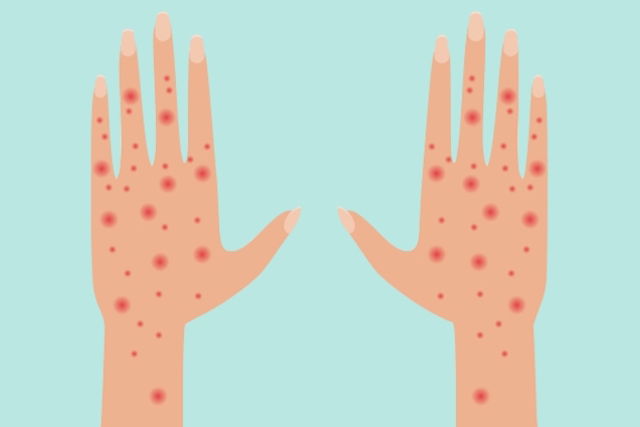
Main symptoms
The most common symptom of scabies is intense skin itching that worsens at night. Other common symptoms include:
- Very intense itching that worsens at night
- Small red blisters on the skin
- Raised, swollen skin
- White lines on the skin, close to the area where the mite is present.
Symptoms of scabies are most common within the skin folds, and can be noted between the fingers and toes, in the armpits, around the waist, breasts, wrists, elbows, groin or buttocks.
The symptoms of the initial infection usually appear within 2 months, however in subsequent cases, symptoms may appear faster, appearing in less than 4 days.
How it's diagnosed
Human scabies is diagnosed by a dermatologist through an assessment of the presenting symptoms, the patient's health history and a physical examination of the skin.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor can perform a dermoscopy exam, as it allows for the skin to be assessed in detail and possibly identify the mite, eggs, larvae and/or feces.
How it is transmitted
Scabies is a very contagious disease that can easily spread from person to person through direct contact of the skin. The female Sarcoptes Scabiei mite lives and deposits her eggs in the outermost layer of the skin, which facilitates transmission.
In addition, this disease can be transmitted even if the patient does not have any symptoms. Even if you do not think you have scabies, you should adopt certain habits to prevent the transmission of these types of illnesses. Some examples include:
- Avoid sharing towels
- Avoid sharing unwashed clothes
- Wash your skin at least once per day
- Avoid direct contact with people who live in unsanitary environments
Clothing that are not washed frequently should be placed inside a closed plastic bag until they are used again, as this will prevent the deposit of mite eggs onto the clothes.
Treatment options
Treatment for scabies should be monitored by a dermatologist, and will vary with the severity of infestation and the patient’s skin type. Nonetheless, treatment is usually completed with medications such as:
- Permethrin: This cream should be applied to the skin to eliminate the mites and eggs. It can be used in adults, pregnant women and children over 2.
- Crotamiton: This can be purchased as a cream or lotion and is applied on a daily basis. It is contraindicated for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Ivermectin: This pill strengthens the immune system and helps to eliminate the mites. It should not be used by pregnant or breastfeeding women, nor by children weighing less than 15 kg (about 33 lb).
Generally, these medications are applied to the entire body, from the neck down. They should stay on the skin for 8 hours, and therefore many patients are advised to apply them prior to bed. In addition, patients should maintain adequate hygiene and wash all clothing, bed linens or towels in hot water after use.
Home remedies for scabies
A great natural remedy to relieve scabies symptoms and facilitate treatment is aloe vera gel. This gel contains properties that soothe the skin and reduce itching while also helping to eliminate the mites. To use natural aloe vera, you should remove the gel from the inside of an aloe vera plant and spread it over affected areas of the skin. Allow it to sit for at least 15 minutes, then remove with water and a mild, pH-neutral soap.
Also recommended: Home Remedies for Scabies: 7 Natural Recipes tuasaude.com/en/home-remedies-for-scabiesIs vinegar good for treating scabies?
Vinegar is not normally recommended for treating scabies, as it is not capable of eliminating the parasite from the skin. Although applying vinegar compresses can sometimes be used to relieve itching, it is not enough to cure scabies. Learn more about other home remedies for itchy skin.
Prevention measures
Some precautions are important to prevent the transmission of scabies, such as:
- Do not share bath towels
- Avoid sharing unwashed clothes
- Wash your skin at least once a day
- Disinfect surfaces shared with several people, such as gym equipment and mats
- Avoid direct contact with people who live in places with poor hygiene conditions.
If you are unable to wash clothes frequently or in a timely manner, they can be placed in a closed plastic bag while they are not being used to prevent mites from sticking to them.
Even when a person has no symptoms but is infected, the disease can be transmitted to other people. Therefore, if a case of scabies is identified in the household, it is important that everyone who has been in direct contact to undergo treatment.
