A rash on the hands from eczema is a type of allergy that can emerge when the hands come in contact with a triggering substance. It causes skin irritation and leads to signs and symptoms like redness and itchiness.
Normally, it is caused by contact with products like soaps, detergents and cleaning products. People who are more likely to get a rash on their hands from eczema are those with a positive family history of this illness, or people who frequently work with certain substances.
If you suspect your rash on your hands is from eczema, you should consult a dermatologist or immune specialist to confirm a diagnosis and start appropriate treatment. The doctor may prescribe antihistamines and anti-inflammatory ointments, as well as recommend avoidance of possibly irritating substances and materials.
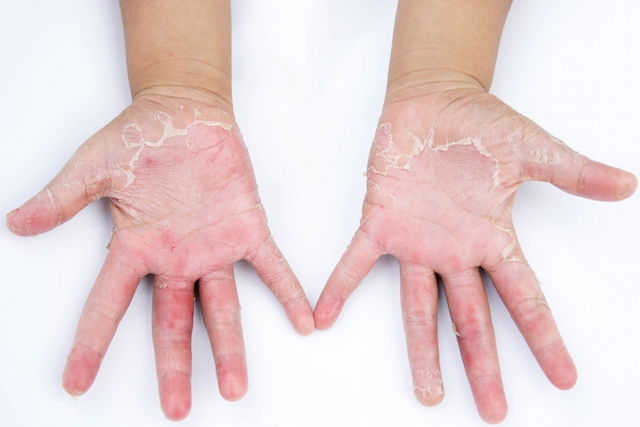
Common symptoms
Symptoms that are typically associated with a rash on the hands include:
- Itching
- Redness
- Dry skin
- Swelling
- Cracked skin
- Flaking skin
- Blisters
- Sensitive skin
- Thicker skin
A rash on the hands can take up to 3 days to develop after initial contact with the irritating product or material. It is common for the rash to affect both hands at the same time, or specific areas of the hands, like the palms or fingertips.
In addition, symptoms like nail deformities, thicker skin and cracked skin tend to emerge is the rash is left untreated.
Possible causes
A rash on the hands is usually caused by contact with chemicals in cleaning products, soaps, detergents, serums and creams. These can irritate the skin, especially if they are scented.
Some of these products remove the skin’s natural defense barrier which lead to dehydration. The skin then becomes drier and even less protected.
Other possible causes of a rash on the hands include using jewelry (like rings and bracelets), using wool or cotton gloves, frequent cold or heat exposure, and constant friction from clothes.
Rashes on the hands are more common in those with a positive family history of eczema. It is also more commonly noted in painters, hairdressers, cleaners and sales associates due to frequent contact with various chemicals.
Can a rash on the hands by triggered by emotions?
A rash on the hands from eczema can worsen or be triggered by emotions like stress or anxiety in some people. Normally, these patients will present with symptoms like excessive worrying and difficulty sleeping. Read more about stress rashes and the symptoms associated with these.
Treatment options
Treatment for a rash on the hands is done with antihistamine medications (like hydroxyzine and cetirizine) and corticosteroid ointments. These medications should be used as prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
Chronic rashes, which is when the rash persists for over 4 weeks and does not resolve with medications, can be treated with medications like azathioprine, methotrexate or cyclosporin.
When the rash on the hands also presents with signs of infection, like pain, intense redness, worsening swelling and wounds with discharge, the doctor may also prescribe antibiotics.
Prescription ointments
Ointments that are prescribed for rashes on the hands typically contain corticosteroids, like betamethasone or dexamethasone. If the rash does not improve with treatment, however, other ointments may be prescribed, like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus.
Other considerations
If you experience a rash on the hands, the following is recommended:
- Use rubber gloves when washing the dishes, washing clothes or using cleaning products. This helps to prevent direct skin contact with chemicals.
- Avoid washing your hands excessively, especially with hot water or scented soaps.
- Apply neutral moisturizing cream after washing your hands.
- Avoid washing your hands to prevent wounds
It is also important to identify the underlying trigger and avoid contact with it. Even fabrics like wool, cotton or nylon, can trigger a rash, as well as soaps, creams or scented oils.
