Endometritis is the inflammation of the uterine lining which commonly occurs with fungal infections or STIs, but can also happen due to allergies to products, a pH change from lack of/excess hygiene, and direct trauma to the region.
It causes symptoms such as vaginal discharge, bleeding that is unrelated to a period, cramping and a feeling that the uterus is swollen. However, some women may present with symptoms only after the condition has progressed to a more serious phase, leading to a late diagnosis.
Inflammation can occur either in the cervix, located at the lower end of the vagina, or in the inner lining, the endometrium, resulting in endometritis, as the images show:
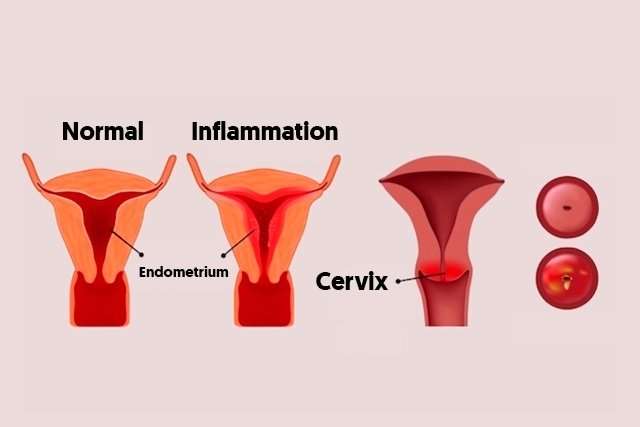
A diagnosis is confirmed by a gynecologist through a pap smear or through examination called colposcopy. Both of these assessments allows the doctor observe internal tissue and collect a specimen for analysis.. Treatment is usually done with pills or ointments, which may be antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, for example.
What are the symptoms
The main symptoms of endometritis may include:
- Bad-smelling yellowish, brown or gray discharge;
- Bleeding during or after sex
- Bleeding unrelated to a period;
- Pain when urinating and during sex;
- Constant pain in the lower part of the belly;
- Feeling of swelling in the lower part of the belly or in the uterus.
However, it is important to remember that these symptoms may also be present in other uterine conditions, such as myoma or uterine polyps, for example.
In addition, pain while urinating and abdominal pain may also be signs of ovarian inflammation.
Causes for uterus inflammation
Some causes that can cause uterine inflammation and endometristis are:
- Sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, or HPV;
- Infectious vaginitis, such as candidiasis or bacterial vaginosis, for example;
- Allergy to condoms, diaphragms or chemicals such as spermicides;
- Lack of hygiene or excessive hygiene in the genital area, especially the overuse of soap, as this changes the vaginal pH and favors the growth of microorganisms that cause diseases;
- Injuries that occur during labor.
It is important to identify the correct cause of endometritis so that proper treatment can be done to avoid the recurrence of the problem.
Uterine inflammation and pregnancy
Inflammation in the uterus makes it difficult for a woman to become pregnant, as it prevent the embryo from implanting itself in the wall of the uterus and developing. However, when it occurs during pregnancy, it usually does not interfere with the development of the fetus if treated properly, If left untreated it can lead to complications such as miscarriage.
What treatment options are available
The treatment for endometritis depends on the underlying cause of the problem. When the inflammation is due to the presence of foreign microorganisms, it may can treated with a course of antibiotic, antiviral or antifungal medication such as nystatin, miconazole, clindamycin or metronidazole. These medications should be used as prescribed. In some cases, sexual partners also need to be treated, to prevent reinfection of the same microorganisms that caused the inflammation.
The gynecologist may also advise cauterization of the cervix to help heal any lesions. If the inflammation in the uterus is caused by an allergy to materials that come into contact with the woman's internal region, such as a condom or a diaphragm, the use of these products should be discontinued and, if necessary, anti-inflammatory drugs can be taken to alleviate pain and help the uterus to recover.
If uterine inflammation is not treated, inflammation can spread to other internal regions, such as the endometrium, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. In these cases, you may need to be treated in a hospital setting with IV medication to better-contain the inflammation.
Home remedies
You should avoid any sexual contact while completing treatment. To complement your prescribed treatment of endometritis, you should also increase your fluid intake (to at least 2 L or half a gallon of water per day). A healthy diet rich in omega 3 (which is present in salmon and sardines), fruits, vegetables and greens will help to speed-up the healing of any inflammation.
Can endometritis become cancer?
If the inflammation in the uterus is caused by certain types of the HPV virus, and it is not properly treated, it is possible for the inflammation to develop into cervical cancer over time. Therefore, whenever there are signs and symptoms that indicate an inflammation, it is important to seek a gynecologist’s help to identify the correct cause and start treatment as soon as possible.








