The first symptom of syphilis is a dry wound that neither bleeds nor hurts and appears after direct contact with another person's syphilis wound. This wound may take 3 to 12 weeks to appear after initial exposure and releases a clear liquid when rubbed.
This wound tends to disappear on its own without any treatment, but this doesn’t mean that the disease has healed; in fact, once the wound has healed, it means the infection has progressed to the second stage.
Syphilis can appear in four different ways: primary, secondary, tertiary and congenital, which occurs when a pregnant woman who has syphilis doesn’t adhere to treatment and passes the disease on to the baby. Each form of syphilis has its own characteristics:
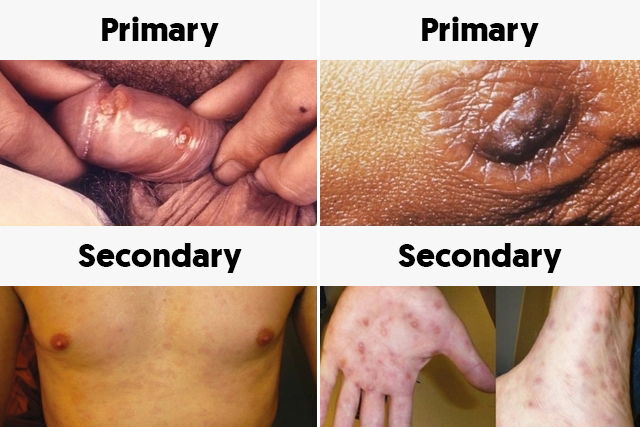
1. Primary syphilis
Primary syphilis is the early stage of the disease, which appears about 3 weeks after the initial infection. This stage is characterized by the appearance of hard lumps or small red lesions in the genital area that end up disappearing within 4 or 5 weeks. They usually do not leave any scars.
In men, these wounds usually appear around the foreskin, while in women they appear on the small lips, or labia minora, and vaginal wall. This wound can also appear in the anus and mouth, and on the tongue, breasts and fingers. Swollen lymph nodes may be noted in the groin or near the affected area during this stage. Learn more about why lymph nodes become swollen in the presence of infections.
2. Secondary syphilis
After the disappearance of the hard lesions, there is a period of inactivity that can last from six to eight weeks. The disease then becomes active once again and affects the skin and internal organs, as the bacteria spreads throughout the body.
The new lesions are characterized as pinkish spots or small brownish-colored lumps that appear on the skin, mouth, nose, palms and soles. Some patients experience intense skin peeling. Other possible symptoms are:
- Swollen lymph nodes throughout the body, but mainly in your genital area;
- Headaches;
- Muscle pain;
- Sore throat;
- Malaise;
- Mild fever, usually below 38 ° C;
- Lack of appetite;
- Weight loss.
This phase continues during the first two years of the disease, and appears as outbreaks that regress spontaneously, but which are longer-lasting.
3. Tertiary syphilis
Tertiary syphilis occurs in people who haven’t been able to spontaneously fight against the disease in its secondary stage or haven’t had the appropriate treatment. In this stage, syphilis is characterized by:
- Largers lesions on the skin, mouth and nose;
- Problems in internal organs: heart, nerves, bones, muscles, liver and blood vessels;
- Constant headaches;
- Frequent nausea and vomiting;
- Neck stiffness, with difficulty in moving the head;
- Convulsions;
- Hearing loss;
- Vertigo, insomnia and stroke;
- Exaggerated reflexes and dilated pupils;
- Delusions, hallucinations, decreased recent memory, difficulty with orientation and doing simple mathematical calculations, as well as in speaking when there is general paresis.
These symptoms usually appear 10 to 30 years after the initial infection when the individual isn’t treated. To avoid complications in other organs of the body, treatment should be done soon after the onset of the first syphilis symptoms.
Symptoms of congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is when the baby is infected with syphilis during pregnancy, which happens when syphilis is not treated during pregnancy.
If left untreated, syphilis can cause miscarriage, malformations or death of the baby at birth. In live babies, symptoms may appear between the first weeks of life and up to more than 2 years after birth, and include:
- Pale red or pinkish round spots on the skin, including the palms and soles;
- Easy irritability;
- Loss of appetite and energy to play;
- Pneumonia;
- Anemia
- Problems with the bones and teeth;
- Loss of hearing;
- Mental disability.
Treatment for congenital syphilis is usually done with 2 injections of penicillin for 10 days or 2 injections of penicillin for 14 days, depending on the child’s age.
Is syphilis curable?
Syphilis is curable and can be easily treated with penicillin injections, but treatment should be started as soon as possible to prevent serious complications in other organs such as the brain, heart and eyes, for example.
How to diagnose syphilis
To confirm the presence of syphilis, the doctor will inspect the patient’s genital area and assess whether the patient has had unprotected sexual contact. If there are no visible wound in the genital area or other parts of the body, the doctor may request a test called VDRL which looks for Treponema pallidum bacteria in the blood.
This test is usually done every trimester for all pregnant women because syphilis is a serious illness that the mother can pass on to the baby, but is easily cured with antibiotics prescribed by the doctor.